If you have a safeguarding or child protection concern please email our Safeguarding team at [email protected].
If you have a concern about your child at school, you can contact your child's Pastoral Manager or our School Office below. This information will be treated in confidence.
Contact name : Ms K. Murphy, Office Manager
E-mail: [email protected]
Telephone: 020 8902 2038 (Switch)
Has something happened that made you feel worried or unsafe?
If you have any concerns about something that made you feel worried or unsafe, please speak with your Pastoral manager. They can offer support and guidance on a number of issues.
Alternatively you can make a report to one of CEOP's Child Protection Advisors, by clicking on the button below:
Each term we publish a safeguarding newsletter to let parents, carers and students know about the most recent issues around safeguarding and keeping safe. Please see the links below to check out some of our previous edtions:
What is Bullying?
Bullying can be physical, sexual, verbal or emotional in nature.
Bullying may be more specifically characterized by:
- An intention to harm: intention suggests that the harm caused by bullying is deliberate, not accidental
- Victimisation distress: bullying causes the victim to suffer mild to severe psychological, social or physical trauma.
- Repetition: bullying is persistent; it happens more than once or has the potential to occur multiple times.
- Power inequity: definitions of bullying often state that bullying includes a real or perceived imbalance of power between the bully and the victim. This characteristic is disputed, as both bullies and victims have reported that the conflict and/or behaviours most commonly occur between two equals.
- Provocation: bullying is proposed to be apart of progressive aggression: motivated by perceived benefits of their aggressive behaviours
The long-term effects of school bullying are numerous, and can include sensitivity, anxiety, and depression.
The following organisations provide further information about bullying.
 |
 |
Types of Bullying
Cyberbullying
Cyberbullying is any bullying done through the use of technology. This form of bullying can easily go undetected because of lack of parental / authoritative supervision. Because bullies can pose as someone else, it is the most anonymous form of bullying. Cyberbullying includes, but is not limited to, abuse using email, instant messaging, text messaging, websites, social networking sites, etc. With the creation of social networks like Facebook, Myspace, Instagram, and Twitter, Cyberbullying has increased.
Disability bullying
It has been noted that disabled people are disproportionately affected by bullying and abuse, and such activity has been cited as a hate crime. The bullying is not limited to those who are visibly disabled, such as wheelchair-users or physically deformed such as those with a cleft lip, but also those with learning disabilities, such as autism and developmental coordination disorder.
There is an additional problem that those with learning disabilities are often not as able to explain things to other people, so are more likely to be disbelieved or ignored if they do complain
Homophobic bullying
Homophobic bullying and homophobic bashing are expressions used to designate verbal or physical actions that are direct or indirect in nature by a person or group against a person who is gay, lesbian, bisexual, transgendered (LGBT), or of questionable sexual orientation, or one who is perceived to be so, because of rumors or fitting homophobic stereotypes. Gay and lesbian youth are more likely to report bullying.
Verbal Abuse
Verbal abuse (also known as reviling) is described as a negative defining statement told to the victim or about the victim, or by withholding any response, thereby defining the target as non-existent. If the abuser does not immediately apologize and retract the defining statement, the relationship may be a verbally abusive one.
In schools a young person may indulge in verbal abuse — bullying (which often has a physical component) to gain status as superior to the person targeted and to bond with others against the target. Generally the bully knows no other way to connect emotionally, i.e., be bonded with others
Physical Abuse
Physical abuse is an act of a person involving contact of another person intended to cause feelings of physical pain, injury, or other physical suffering or bodily harm. In most cases, children are the victims of physical abuse, but adults can also be victims, such as in a domestic context. Alternative terms sometimes used include physical assault or physical violence, and may also include sexual abuse. Physical abuse may involve more than one abuser and more than one victim.
Physically abused children are at risk for later interpersonal problems involving aggressive behavior, and adolescents are at a much greater risk for substance abuse. In addition, symptoms of depression, emotional distress, and suicidal ideation are also common features of people who have been physically abused. Studies have also shown that children with a history of physical abuse may meet DSM-IV-TR criteria for posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Parental bullying of children
Parents who may displace their anger, insecurity, or a persistent need to dominate and control upon their children in excessive ways have been proven to increase the likelihood that their own children will in turn become overly aggressive or controlling towards their peers.The American Psychological Association advises on its website that parents who may suspect that their own children may be engaging in bullying activities among their peers should carefully consider the examples which they themselves may be setting for their own children regarding how they typically interact with their own peers, colleagues, and children.
School bullying
Bullying can occur in nearly any part in or around the school building. Though it may occur more frequently during physical education classes and activities such as recess. Bullying also takes place in school hallways, bathrooms, on school buses and while waiting for buses, and in classes that require group work and/or after school activities. Bullying in school sometimes consists of a group of students taking advantage of or isolating one student in particular and gaining the loyalty of bystanders who want to avoid becoming the next target. In the 2011 documentary Bully, we see first hand the torture that kids go through both in school and while on the school bus. As the movie follows around a few kids we see how bullying affects them both at school as well as in their homes. While bullying has no age limit, these bullies may taunt and tease their target before finally physically bullying them. Bystanders typically choose to either participate or watch, sometimes out of fear of becoming the next target.
Bullying can also be perpetrated by teachers and the school system itself; there is an inherent power differential in the system that can easily predispose to subtle or covert abuse (relational aggression or passive aggression), humiliation, or exclusion — even while maintaining overt commitments to anti-bullying policies.
School teachers are commonly the subject of bullying, but they are also sometimes the originators of bullying within a school environment.
Sexual bullying
Sexual bullying is "any bullying behaviour, whether physical or non-physical, that is based on a person's sexuality or gender. It is when sexuality or gender is used as a weapon by males or females towards others - although it is more commonly directed at females. It can be carried out to a person's face, behind their back or through the use of technology.
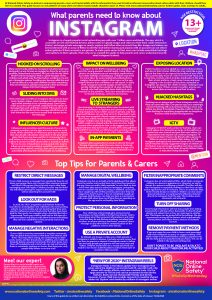
The posters below from National Online Safety are designed specifically for parents and provide some useful information about different online services to help you keep your children safe online.
- Discord
- Game Consoles
- Webcams
- Voice Activated Service
- Screen Grabs
- Lifestyle Sites
- Fitness Trackers
- Age Rating